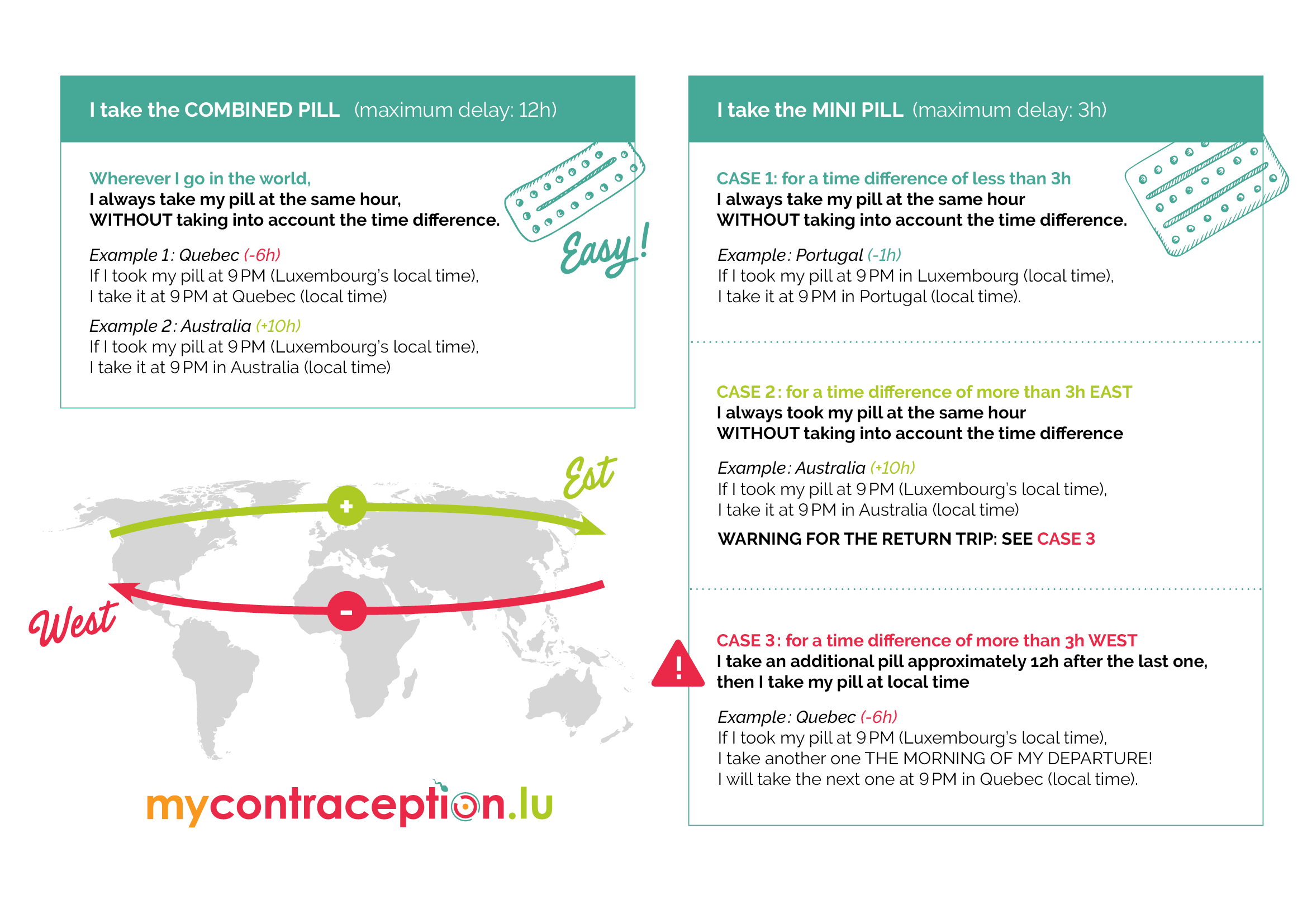
The Combined Pill
Also called combined oral contraception (COC), the combined pill contains both progesterone and oestrogen.
* Practical effectiveness: when measured under conditions of current use (taking into account omissions, failures, etc.)
** Theoretical effectiveness: when observed under conditions of perfect use (without problems of use and without interaction with other medicine)
Source: effectiveness percentages are taken from WHO (2018)
HOW DOES IT WORK?
Each pill contains two types of hormones. The pill blocks ovulation, thickens the cervical mucus (which makes it harder for sperm to pass through) and prevents the lining of the uterus from developing to accommodate a possible fertilized egg. There are several types of combined pills. Usually, the pack contains 21 hormone pills and 7 days off.
INTERESTING FIGURES AND DETAILS
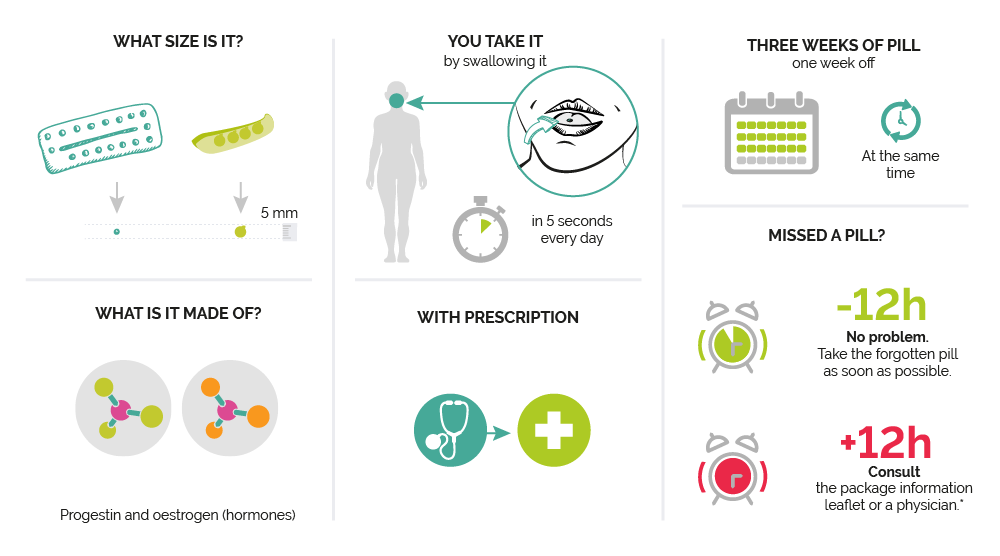
HOW TO TAKE THE PILL?
STEP 1
Go to a physician or gynaecologist and then to a pharmacy with your prescription.
STEP 2
It is the first time you take the pill, or you are back on the pill after a break? Start the pack on the first day of your period.
You would like to start the pill right away? There are certain conditions to respect. Ask your physician for more information.
STEP 3
Take your pill at the same time every day. You are no longer protected if you are sick within the 4-hours following the intake (diarrhea, vomiting). Take a new pill as soon as possible in that case.
STEP 4
In case of 21 pills pack, there is a 7-day break during which you will have your period. Start a new pack of 21 pill after the 7 days break even if there is still bleeding. For example, if you start a pack on Tuesday, you will have your period 3 weeks later on a Tuesday and you will start a new pack the following Tuesday.
In the case of 28 pills pack, there ir no break, and you start a new pill pack as soon as the previous end (even if there is still bleeding)
WHERE TO GET IT?
Starting 1 April 2023, this contraceptive is delivered free of charge in any Luxembourg pharmacy with a medical prescription to people affiliated with the National Health Fund, with no age limit.
For more information: click here.
This contraceptive can also be delivered for free at the Family Planning, including to people not covered by the National Health Fund.
The combined pill costs on average between 18-166€* per year (13 cycles).
*(This price is an average indication which may vary).
ADVANTAGES
- The combined pill allows a more regular menstruation cycle (of 28 days)
- It is possible to postpone your period by taking two packs without a break. Some combined pills are taken continuously, which then stops periods.
- You do not need to think about it every time you are having a sexual intercourse, but you should think about taking it every day.
GOOD TO KNOW
- The combined pill does not protect against sexually transmitted infections. Therefore, remember to use condoms.
- The pill is less effective if you vomit or have diarrhea 4 hours after taking it. Effectiveness can also be altered while taking certain medications such as some antibiotics. For any question, do not hesitate to contact your physician or pharmacist.
- With a combined hormonal contraceptive (such as the combined pill), there is an increased risk of venous thrombosis. This is a clot formation in the veins that can be dangerous. This risk is higher during the first year of using the contraceptive and when tacking it back after a break of more than 4 weeks.
- Not suitable for breastfeeding women.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
When you first take the pill, how long does it take to work?
When you start taking the pill on the first day of your cycle (1e day of your period), the pill is effective immediately. If you start taking the pill in the middle of an ongoing cycle, it is advisable to use another method of contraception for at least 7 days before the pill becomes effective.
When I take the pill, is having my period a proof that I am not pregnantl?
No. You can have your period while you are pregnant although you are on the pill. This is because bleeding on the pill is called “withdrawal bleeding” and is triggered by some of the (white, or placebo) tablets of the pill itself, so it is not a real period. Menstruation on the pill is therefore not a reliable indicator of whether or not you are pregnant. You will need to take a pregnancy test 19 days after unprotected intercourse to find out if you are pregnant or not.
What is the difference between the combined pill and the mini-pill?
The combined pill (estroprogestative pill) contains 2 hormones: a progestin and an estrogen. The mini-pill (microprogestogen pill) contains only progestin hormones. Although both types of pills have the same level of effectiveness when taken correctly, it should be noted that some people feel more comfortable with one or the other type of pill. There are many different combinations of hormones and amounts, so don’t hesitate to discuss any side effects of the pill: there are many choices! 🙂
Why are the pill packs for 28 days?
For a long time, menstrual cycles were wrongly modelled on the lunar cycles, which are 28 days long. This number has therefore been kept as the average number of days in a menstrual cycle, even though this number varies from person to person, actually ranging from 21 to 36 days on average.
I forgot to take my pill, what should I do?
Less than 12h :
If you forget to take the combined pill for less than 12 hours, take the missed pill as soon as possible.
More than 12h :
If you did not have sex on the day you forgot to take the pill and/or the previous 5 days, continue the pack, but use a condom for the next 7 days. You must take 7 consecutive coloured pills after a missed pill to be protected. If you come to the end of your pack after a missed pill, you should not take the ‘white’ / placebo pills (those taken during your period), but start directly with a new pack. If your pill type does not have a placebo pill, do not take a 7-day break and start a new pack directly.
If you had sex on the day you forgot to take the pill and/or in the previous 5 days, consult a health professional to find out what to do. In the meantime, continue to take the pill, and if you have sex, use a condom.
Note: If you forgot a white/placebo pill, there is no risk of pregnancy. Simply continue to take the next pills until you start a new pack.
How can I remember to take the pill every day?
In order to remember to take the pill, it is advisable to link it to some daily routine, such as brushing your teeth, showering, or any other daily action. You can also set an alarm on your phone at a fixed time or put a visual reminder, such as a note on the bathroom mirror. If you are in a relationship with a regular partner, this person can also take part in this reminder management.
You can also carry a spare pack of pills with you in case of unforeseen circumstances (if you don’t return home), and keep the prescription with you in case you forget to take it while travelling or on holiday.
Also try to choose a time that allows you time to notice if you have forgotten your pill, so that you can make up for it (within 12 hours for the combined pill, within 3 hours for the mini-pill).
How can I remember to take the pill every day?
In order to remember to take the pill, it is advisable to link it to some daily routine, such as brushing your teeth, showering, or any other daily action. You can also set an alarm on your phone at a fixed time or put a visual reminder, such as a note on the bathroom mirror. If you are in a relationship with a regular partner, this person can also take part in this reminder management.
You can also carry a spare pack of pills with you in case of unforeseen circumstances (if you don’t return home), and keep the prescription with you in case you forget to take it while travelling or on holiday.
Also try to choose a time that allows you time to notice if you have forgotten your pill, so that you can make up for it (within 12 hours for the combined pill, within 3 hours for the mini-pill).
What if I have unpleasant side effects from the pill?
Certain side effects may occur when taking hormonal contraception (heavier or lighter periods, migraines, breasts pain, bleeding between periods, impact on sexual desire, etc.). These side effects are often harmless, but if they become bothersome, your pill may not be suitable. In this case, consult a health professional.
There are so many different pills available, and it is common to have to try several before finding one that suits you well.
If you wish to stop your hormonal contraception, it is recommended that you see a health professional before stopping so that you can plan the transition to another contraception. If, however, you wish to stop your contraception immediately, you can use a temporary contraception (e.g. condom) until you see a health professional.
Is it safe to take the combined pill if you smoke?
Smoking is a contraindication to taking estrogen-progestin hormonal contraceptives (combined pill, patch, vaginal ring) when you have been a smoker for several years. Indeed, the natural ageing of blood vessels combined with smoking and estrogen increases the risk of blood clots, which are responsible for cardiovascular accidents (brain), phlebitis (legs) or pulmonary embolisms (lungs). As a general rule, at the age of 35 onwards, smokers using oestrogen-progestin contraception should consider other contraceptives to reduce these health risks. Women under the age of 35 can use estrogen-progestin contraception if they have no associated cardiovascular risk factors. Do not hesitate to ask your physician if you are in this situation: several possibilities exist! Among others, it is possible to use the mini-pill, the IUD or the implant (containing only progestative).
Can the pill reduce acne?
The pill can have an effect on acne but this may result in an increase or decrease. Contraception can have an effect on acne but it is important to note that it is not a treatment for acne. If you have severe acne, see a specialist health professional (e.g. dermatologist, etc.). Also, if your pill increases your acne, you can talk to your physician about taking a different pill.
Is a gynecological examination required to receive a prescription for the pill?
No. The only hormonal contraception that requires a gynecological examination is the hormonal or copper coils (the IUD/IUS). However, a physician’s consultation is necessary to check that you do not have any contraindications to taking the pill. You can go to your physician or the Family Planning to get a prescription for the pill.
Do I have to see a physician to get a prescription refilled?
In Luxembourg, you normally need a prescription from a general practitioner or gyneacologist to buy the pill in a pharmacy. However, if you are unable to make an appointment with your physician or gyneacologist, he or she may write you a prescription which you simply collect at a cost of approximately €15, which is reimbursable by the CNS.
If you are unable to obtain a prescription, you can go to your usual pharmacy and, depending on the pharmacist’s decision, it is sometimes possible to provide your contraception without a prescription if bought regularly for some time at the same pharmacy. However, in this case, you will have to pay 100% of the price of the contraception. You can also go to the Family Planning to get your contraception at a reduced price, or even free of charge depending on the situation.
I am going on a trip for several months. Can I get several packs of pills, patches or rings?
Yes, it is possible to buy up to 6 months of contraception if you are entitled to reimbursement from the CNS (currently: women under 30 years of age, at 80%). Please note that some pills are also available in 13-month packs. If you have any questions about this, please contact your physician.
If you are no longer covered by the CNS because of your age, it is possible to obtain up to 1 year of contraception refill.
Are there any medicines that are contraindicated when taking the pill?
Some medicines can reduce the effectiveness of the pill. This is the case with anti-tuberculosis drugs, epilepsy treatment, certain plants (millepertuis) and certain antibiotics. If you have diarrhoea or vomiting within 4 hours of taking the pill, you may have expelled the hormones and the effectiveness of your pill may be impaired. You should therefore take another pill. For more information on this subject, do not hesitate to speak to your physician or pharmacist, or to refer to your pill’s instructions.
Can I get pregnant during the week I stop taking the pill between packs?
No. The pill is intended for 21 days followed by a 7-day break. However, it is important to respect the 7-day break and to start a new one immediately! Otherwise there is a risk of pregnancy.
In theory, menstruation (withdrawal bleeding*) occurs during this 7-day break. However, it is possible that your period is a little delayed or not quite finished after the 7th day. This does not matter, and you should still start a new pack of pills after the 7th day.
* Bleeding, or withdrawal haemorrhage, is the monthly loss of blood when hormonal contraception is stopped. They are not “periods” in the same way as those that occur without hormonal contraception and are generally shorter.
If I get pregnant while taking the pill, is it dangerous for my health or my pregnancy?
No. If you decide to continue the pregnancy, you can simply stop taking the pill as it will no longer be needed. Taking the pill at the beginning of your pregnancy will not affect the embryo or the fetus.